All you need to know about sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder that is characterized by repeated stops and starts of one’s breathing pattern.
Symptoms
People with sleep apnea usually have symptoms that include; loud snoring, noisy and labored breathing when asleep, episodes of paused breathing, waking with a dry mouth, gasping for air when sleeping, morning headaches and insomnia. Some patients also have night sweats and frequently wake up to urinate. Patients with this condition wake up feeling tired and irritable.
Causes
There are two types of sleep apnea, namely; Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Central Sleep Apnea. Very few people have mixed apnea which is a combination of both types. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the airway is narrowed, owing to the muscles in the back of the throat relaxing. This causes insufficient air to reach one’s lungs, lowering the levels of oxygen in the blood. This causes the brain to realize that you are not able to breathe which leads to a brief awakening with choking, a gasp or a snort, that makes you reopen the air passage. This is not usually remembered but it prevents one from getting a night of restful sleep.
Central Sleep Apnea
This form of apnea is caused by the lack of signals from the brain to the muscles that control breathing. This form of the disorder is less common. It causes the levels of oxygen in the blood to drop, which is called hypoxemia. There is also an increased level of carbon dioxide which is called hypercapnia. This hypoxemia and hypercapnia have further effects on the body which vary in severity depending on the extremity of the condition.
Risk factors
The risk factors for having this condition are obesity, larger than average neck circumference, narrowed airway, being over 40 years of age, family history of apnea, the use of alcohol, sedatives or tranquilizers, being a smoker, having nasal congestion. Men and postmenopausal women are more like to develop this disorder.
Complications
Sleep apnea disorder causes complications such as fatigue, irritability, drowsiness, moodiness, depression, elevated blood pressure, heart problems, increased risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, increased risk of metabolic syndrome and abnormal liver function. People with sleep apnea are also more likely to face problems when undergoing medical procedures and surgery as they are prone to breathing problems, especially when sedated. There is also the problem of disturbing the sleep of one’s partner. It has been found that sleep-deprived drivers with obstructive sleep apnea are 12 times more likely to have a car accident than the average person.
Treatment
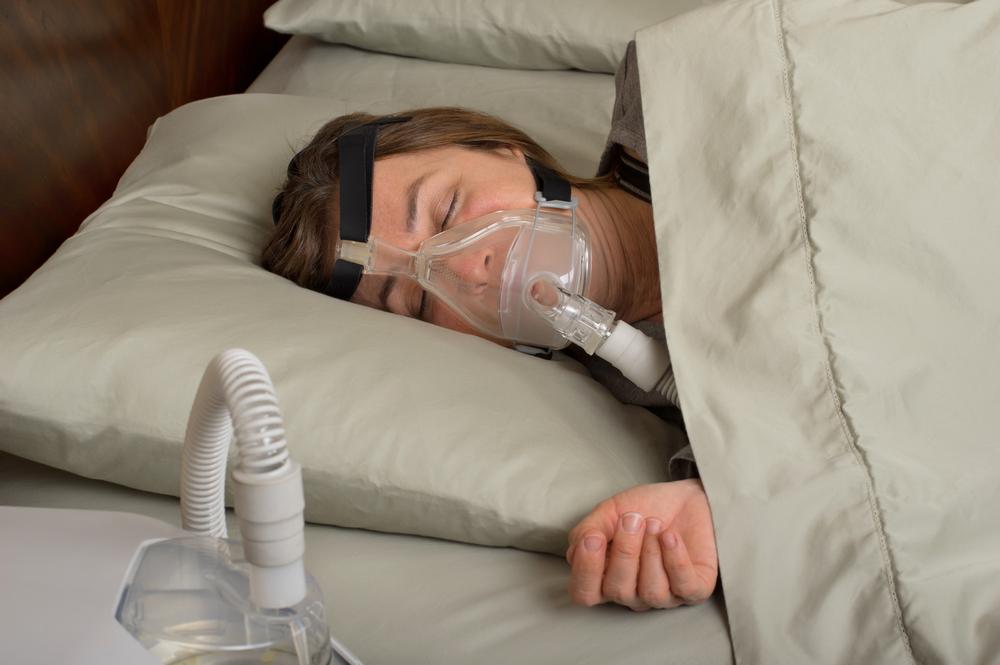
Lifestyle changes can help to relieve the symptoms of the disorder to a certain extent. One is advised to lose excess weight and sleep on one’s side and not on the back. Quitting alcohol and smoking is advisable. In some cases, continuous positive airway pressure device (CPAP) or an oral appliance has to be used to prevent the narrowing and closing of one’s airway when sleeping. Neurostimulation, diaphragm pacing, nasal bandages, medications, and oral pressure therapy are used to reduce the symptoms of this disorder. Surgery to remove anatomical causes of obstruction is also used as the last resort to treat sleep apnea.