Cystic fibrosis – Causes, risk factors and symptoms
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a condition which affects the cells responsible for the production of sweat, mucus, and digestive fluids. It is a rare condition that affects around 30,000 people in the country. Roughly 1000 new cases are diagnosed each year.
All newborns in the country are tested for cystic fibrosis. The diagnosis is a multistep process that includes a newborn screening, a sweat test, a carrier test, and a genetic test. Clinical evaluation should be done at a CF Foundation-accredited care center. More than 75% of the people with this condition are diagnosed by the age of 2.
What are the causes of cystic fibrosis?
In people with cystic fibrosis, mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene makes the CFTR protein dysfunctional. When the protein does not work as it should, it cannot move chloride to the cell surface. The presence of chloride in the cell surface is essential as water is attracted to it because of which it dilutes the fluids. As dilution of mucus, sweat, and digestive fluids does not take place, these fluids become thick and glue-like.
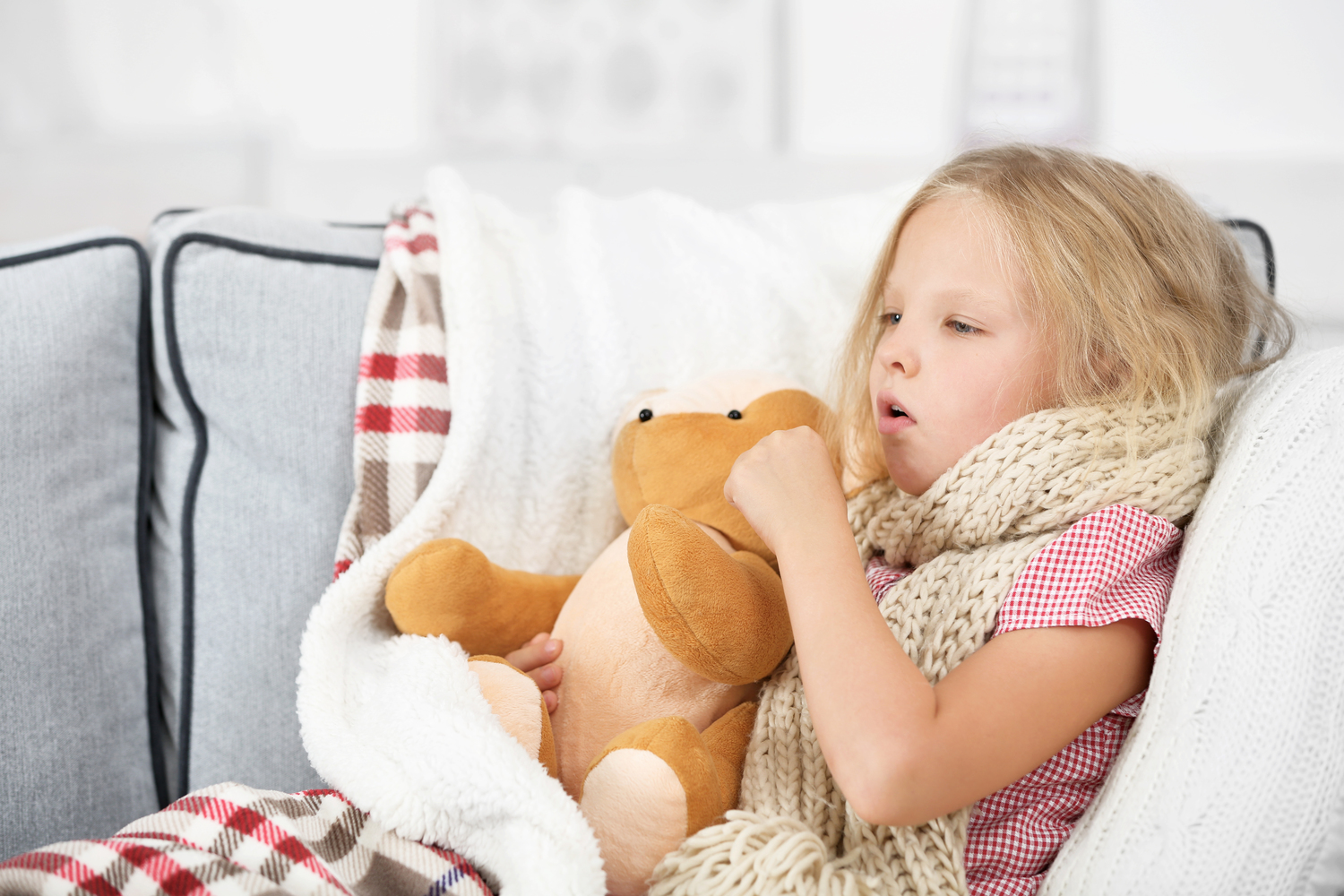
As these fluids become thick, they block the ducts and tubes through which they flow. Mucus will build up in the airways, and as a result, the patient may face breathing problems. Additionally, the mucus traps germs and becomes a breeding place for infections. Severe lung damage can occur due to the formation of cysts and fibrosis; cystic fibrosis gets its name due to this complication.
What are the risk factors for cystic fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis is not contagious. To develop this condition, a child needs to get a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. If a kid inherits it from only one parent, they may not have the symptoms but may be a “carrier” of the gene. Carriers of this gene can pass cystic fibrosis on to their children. Around 10 million people in the country are carriers of cystic fibrosis. If two carriers have a baby, there’s a 25% chance that their baby will be born with cystic fibrosis. Women who are pregnant or couples who are planning a pregnancy can get tested for the CFTR gene to determine the risk of their child being born with the problem. Testing is performed on both parents, and if there is a risk, the fetus is tested too.
Cystic fibrosis is more common among people of Northern European ancestry and is least common in Africans and Asians.
Signs and symptoms of cystic fibrosis
The main signs of cystic fibrosis are salty-tasting skin, poor growth, and weight gain in spite of limited food intake. Accumulation of thick and sticky mucus can cause frequent chest infections and cough. Poor growth and weight in children, as compared to their peers, is one of the indicators of this condition. It is critical to get treat cystic fibrosis at the earliest to improve the quality of life and lengthening the lifespan of the individual.