Diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder
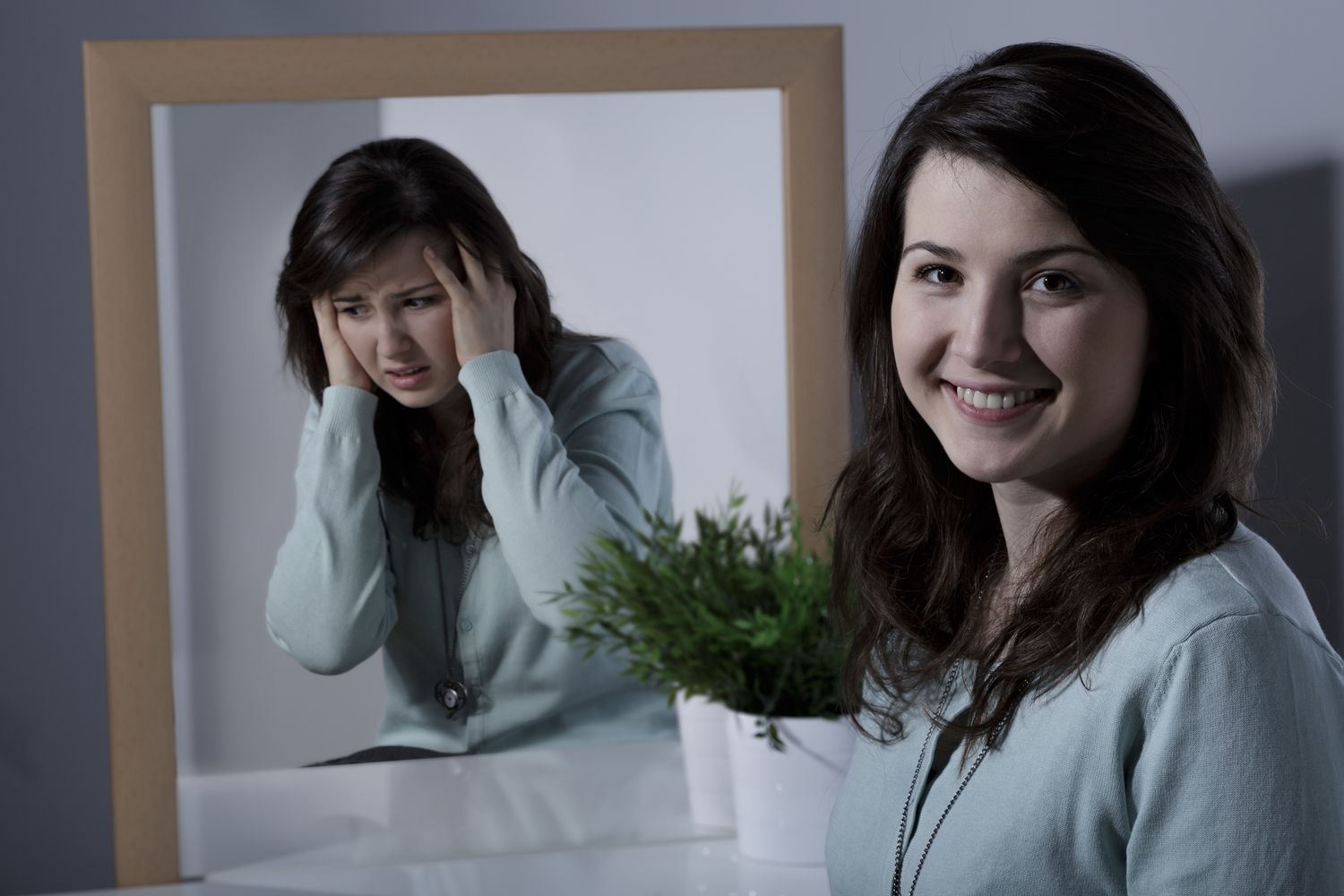
Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that causes extreme fluctuations in mood. It is also known as manic-depressive disorder. When one becomes depressed, one may feel sad or hopeless and lose interest or pleasure in most activities. When the mood shifts to mania or hypomania (less extreme than mania), one may feel euphoric, full of energy or unusually irritable.
Mood swings can affect sleep, energy, activity, judgment, behavior, and the ability to think clearly. Some people may rarely experience these mood swings while others may face them multiple times a year. Most people will experience some emotional symptoms between episodes. However, some may not experience any signs. Although bipolar disorder is a lifelong condition, one can manage the mood swings and other symptoms by following a treatment plan.
Diagnosis
- Physical examination: A doctor may conduct a physical examination and lab tests to identify any medical problems that might be causing the symptoms of bipolar disorder.
- Psychiatric assessment: The patient might be referred to a psychiatrist, who will talk to them about their thoughts, feelings, and behavior patterns. One might also need to fill out a physiological self-assessment or questionnaire. With the patient’s permission, family members or close friends may be asked to provide information about the symptoms.
- Mood charting: One might be asked to keep a daily record of their moods, sleep patterns or other factors that could help with the diagnosis and finding the right treatment.
- Criteria for bipolar disorder: The psychiatrist may compare the symptoms with the criteria for bipolar and related disorders mentioned in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). It is a handbook used by professionals as the authoritative guide for diagnosing mental disorders.
Treatment
Medications
Recommended medications may include
- Mood stabilizers such as lithium
- Antipsychotics like olanzapine
- Antidepressants and antipsychotics such as fluoxetine-olanzapine
- Benzodiazepines, a type of anti-anxiety medication, may be used for short term treatment.
Psychotherapy
- Cognitive behavioral therapy: It is a type of psychotherapy where the patient and the therapist discuss ways to manage bipolar disorder. The therapist will make the patient understand their thinking patterns and also help them come up with positive coping strategies.
- Psychoeducation: It is a type of counseling that helps the person suffering from bipolar disorder and their loved ones understand the disorder.
- Interpersonal and social rhythm therapy (IPSRT): IPSRT focuses on regulating daily habits such as sleeping, eating, and exercising. Balancing these everyday activities can help manage this disorder.
Other treatment options include:
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
- Sleep medications
- Supplements
- Acupuncture
Lifestyle changes for managing bipolar disorder
Some simple steps can help a patient manage their symptoms of bipolar disorder:
- Maintain a routine for eating and sleeping
- Learn to recognize mood swings
- Ask a friend or relative for support in the treatment plan.
- Stay active
It is important to keep an eye out for the common symptoms of this condition to get an early diagnosis and begin an effective treatment plan.