Treatments and medications for ear infection
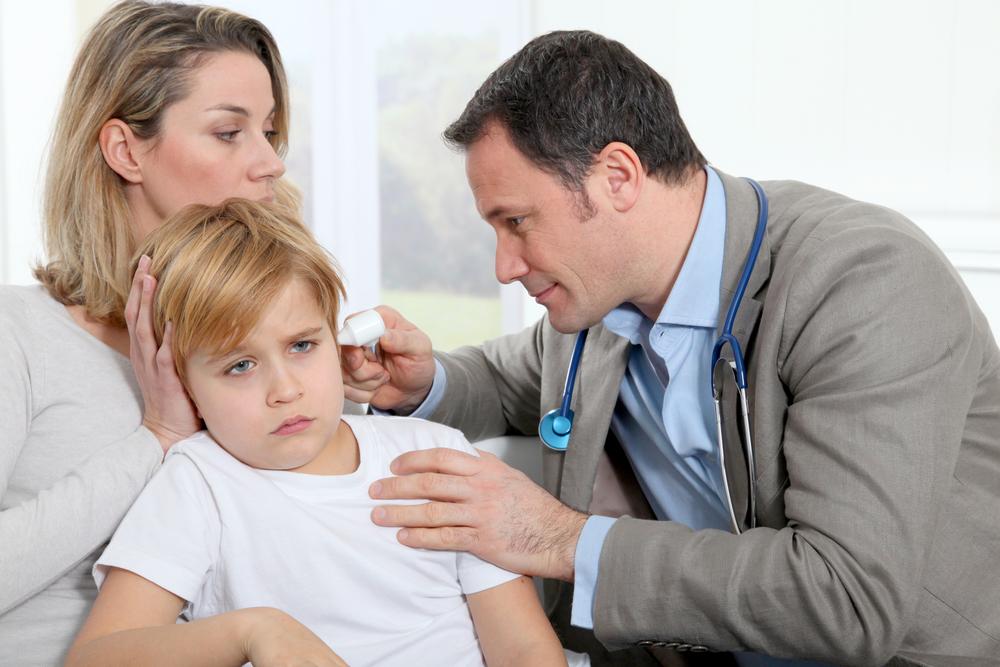
Ear infections that occur in the space behind the eardrum (middle ear) are called otitis media. Ear pain is the most troublesome symptom of ear infection. In most cases, ear infections resolve within 2 to 3 days.
If the pain or any of the other symptoms seem to continue, it is better to check with the doctor for further treatment and medications. Some of the following medications and treatments are effective in relieving the symptoms of ear infection:
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are effective medicines that can kill bacteria. They can be given in the form of ear drops or in the form of oral medicines. Ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin-dexamethasone (Ciprodex) are the commonly preferred antibiotic ear drops. Generally, ear drops are safer and much effective for ear infections. However, oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin can also be effective and successful for treating a ear infection. Other oral medications may include cephalexin (Keflex), sulfamethoxazole, cefdinir, cefpodoxime, cefuroxime, or ceftriaxone. The dosage of these oral antibiotics depends on the severity of the ear infection.
Over-the-counter (OTC) therapies: The doctor may even prescribe a few over-the-counter medications to relieve the pain. Usually, OTC medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen are advised for children. The dosage of ibuprofen for children is 4 to 10 mg every 6 to 8 hours based on the severity of the infection or the pain. Adults are advised with a dosage of 200 to 400 mg every 6 hours. Similarly, the dosage of acetaminophen also depends on the age group of the patient.
Myringotomy (draining of the fluids): If the bacteria has caused serious infection, the fluid remains in the ear for a longer period of time and cannot drain easily. This will lead to a small surgical procedure called myringotomy. The doctor or the surgeon creates a tiny hole in the eardrum, which helps in the suction of fluid or pus out of the middle ear. The next step of this procedure is placing a tiny tube in the opening of the eardrum. This will help in ventilation of the middle ear and prevent further fluid accumulation. Generally, this tube stays in place for about 6 to 18 months, and then it falls out on its own. The tiny hole that is made in the eardrum typically closes up again after the tube is removed.
Natural remedies: During the early stages of pain, you can follow certain steps to ease the symptoms and to reduce the pain caused by a ear infection.
- A warm compress – Compressing a warm and slightly wet cloth over the infected area brings comfort and lessens the pain.
- Gargling – Salt water usually appeases a raw or dry throat, and may help in clearing the blockages of the Eustachian tubes.
- Standing straight – Holding your head upright and standing straight may help in draining the fluids out of the middle ear. This, in turn, reduces the symptoms of a ear infection.
The treatments for ear infections generally continue up to 7 days. In certain cases, due to heavy ear infections, the treatment may continue up to 10 days. Washing hands regularly, avoiding contact with people who have a cold or allergies, and keeping your ears clean are the basic tips to avoid ear infections.